India is rapidly moving towards complete digitisation and is one of the fast mushrooming economies in the world. Although our education system is yet to achieve the global standards of excellence, it is progressing at a steady pace. Education was given great importance in ancient India; the Nalanda University – the oldest university in our country – was established in the 5th century CE and is said to have been flourishing until 1200 CE. Further, even under the British rule, Indians had a strong desire for education and intellectual growth which led to the establishment of several universities during that era. Here’s a look at some of the legacy universities in the country that are still thriving today.
India is rapidly moving towards complete digitisation and is one of the fast mushrooming economies in the world. Although our education system is yet to achieve the global standards of excellence, it is progressing at a steady pace. Education was given great importance in ancient India; the Nalanda University – the oldest university in our country – was established in the 5th century CE and is said to have been flourishing until 1200 CE. Further, even under the British rule, Indians had a strong desire for education and intellectual growth which led to the establishment of several universities during that era. Here’s a look at some of the legacy universities in the country that are still thriving today.
Senate of Serampore College (Estb. 1829)
 Located in Serampore in West Bengal, the Senate of Serampore College was granted the ‘university’ status in 1829. Thereby, Serampore became the first institution to have obtained the status of a university in India. The university was founded by the missionaries Joshua Marshman, William Carey and William Ward with an aim to provide quality education in Arts and Science streams to students hailing from all communities and walks of life. The university presently offers diploma, graduate, post graduate and doctoral programmes in the discipline of Theology.
Located in Serampore in West Bengal, the Senate of Serampore College was granted the ‘university’ status in 1829. Thereby, Serampore became the first institution to have obtained the status of a university in India. The university was founded by the missionaries Joshua Marshman, William Carey and William Ward with an aim to provide quality education in Arts and Science streams to students hailing from all communities and walks of life. The university presently offers diploma, graduate, post graduate and doctoral programmes in the discipline of Theology.
University of Mumbai (Estb. 1857)
 The University of Mumbai was established in 1857 in accordance with “Wood’s despatch” drafted by Sir Charles Wood in 1854. Currently, the university has three campuses across Mumbai – at Kalina, Thane Sub and Fort and one outside Mumbai. The main campus is sited at Kalina, Santacruz. The university has 711 affiliated colleges and offers diplomas, certificate courses and graduate, postgraduate and research programmes in various disciplines such as arts, commerce, and science, medical and engineering.
The University of Mumbai was established in 1857 in accordance with “Wood’s despatch” drafted by Sir Charles Wood in 1854. Currently, the university has three campuses across Mumbai – at Kalina, Thane Sub and Fort and one outside Mumbai. The main campus is sited at Kalina, Santacruz. The university has 711 affiliated colleges and offers diplomas, certificate courses and graduate, postgraduate and research programmes in various disciplines such as arts, commerce, and science, medical and engineering.
University of Madras (Estb. 1857)
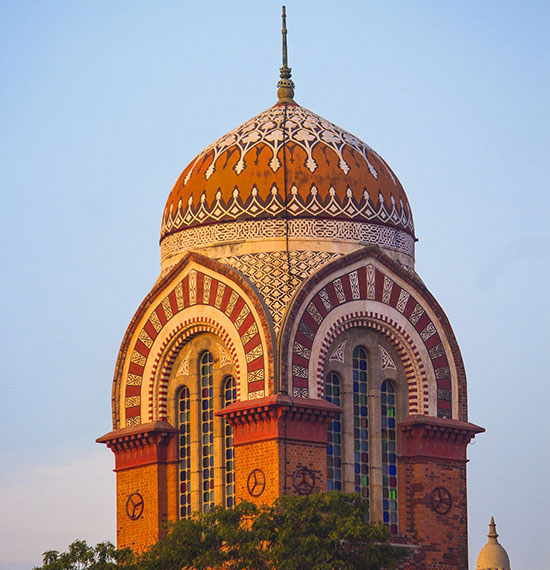 Established in 1857, the University of Madras boasts six campuses at Chepauk, Marina, Guindy, Taramani, Maduravoyal and Chetpet in the city of Chennai formerly called Madras. A public petition signed by nearly 70,000 residents in 1839 initiated for a university that could provide higher education in Madras presidency. The university today boasts 109 affiliated colleges and 52 approved research institutions. At present, the university houses 73 academic departments covering diverse areas such as sciences, social sciences, humanities, management and medicine.
Established in 1857, the University of Madras boasts six campuses at Chepauk, Marina, Guindy, Taramani, Maduravoyal and Chetpet in the city of Chennai formerly called Madras. A public petition signed by nearly 70,000 residents in 1839 initiated for a university that could provide higher education in Madras presidency. The university today boasts 109 affiliated colleges and 52 approved research institutions. At present, the university houses 73 academic departments covering diverse areas such as sciences, social sciences, humanities, management and medicine.
University of Calcutta (Estb. 1857)
 Recognised as a ‘five-star university’ within India and accredited “A” Grade by National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), the University of Calcutta is renowned across the world. Its alumni and faculty include four Nobel laureates — Ronald Ross, Rabindra Nath Tagore, CV Raman and Amartya Sen. The university presently has 14 campuses and 65 departments organised into eight faculties in almost all streams of arts; commerce; and science. The university has the highest number of students who have cleared the doctoral entrance eligibility exam in Natural Science and Arts.
Recognised as a ‘five-star university’ within India and accredited “A” Grade by National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC), the University of Calcutta is renowned across the world. Its alumni and faculty include four Nobel laureates — Ronald Ross, Rabindra Nath Tagore, CV Raman and Amartya Sen. The university presently has 14 campuses and 65 departments organised into eight faculties in almost all streams of arts; commerce; and science. The university has the highest number of students who have cleared the doctoral entrance eligibility exam in Natural Science and Arts.
Aligarh Muslim University (Estb. 1875)
 This university was set up by Sir Syed Ahmad Khan – the great Muslim reformer and statesman, in 1875 as Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College in 1875 and became Aligarh Muslim University in 1920. Post-Indian War of Independence of 1857, Ahmad Khan thought it that it was important for Muslims to get the benefits of higher education so that they could progress and gain good positions in the government. Sprawled over 1154 acres, the university boasts one of the biggest campuses in India and offers more than 300 courses in various subjects. A fully residential university, it has 13 faculties, 7 constituent colleges, 15 centres, 3 institutes and 10 schools under it.
This university was set up by Sir Syed Ahmad Khan – the great Muslim reformer and statesman, in 1875 as Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College in 1875 and became Aligarh Muslim University in 1920. Post-Indian War of Independence of 1857, Ahmad Khan thought it that it was important for Muslims to get the benefits of higher education so that they could progress and gain good positions in the government. Sprawled over 1154 acres, the university boasts one of the biggest campuses in India and offers more than 300 courses in various subjects. A fully residential university, it has 13 faculties, 7 constituent colleges, 15 centres, 3 institutes and 10 schools under it.
Panjab University, Chandigarh (Estb. 1947)
 The present-day Panjab University had its origins with the University of Punjab that was established in British India in 1882 at Lahore currently in Punjab, Pakistan. However, after the partition in 1947, the university was divided into two – for Indian Punjab and Pakistani Punjab. Thereafter, a new university was promoted in 1947 and in order to distinguish the two, the university in India side of Punjab was rechristened to Panjab University. The university boasts 188 affiliated colleges spread over the eight districts of Punjab state and Chandigarh. The university has 78 departments, 15 centres/chairs on the campus and six constituent colleges.
The present-day Panjab University had its origins with the University of Punjab that was established in British India in 1882 at Lahore currently in Punjab, Pakistan. However, after the partition in 1947, the university was divided into two – for Indian Punjab and Pakistani Punjab. Thereafter, a new university was promoted in 1947 and in order to distinguish the two, the university in India side of Punjab was rechristened to Panjab University. The university boasts 188 affiliated colleges spread over the eight districts of Punjab state and Chandigarh. The university has 78 departments, 15 centres/chairs on the campus and six constituent colleges.
Allahabad University (Estb. 1887)
 Allahabad University is the fourth oldest modern university of India that was established in 1887 soon after the Presidency universities of Calcutta, Bombay and Madras were decreed in 1857. The university is the alma mater of three former prime ministers – Gulzari Lal Nanda, Chandra Shekhar and VP Singh, one president, two vice presidents, well-known authors, artists and senior bureaucrats. Once known as the Oxford of the East, the credit for conceiving a large Central College at Allahabad, eventually to develop into a university, goes to Sir William Muir. The campus is spread around the city with separate science and arts faculties and 10 affiliated colleges. (A special report on Allahabad University has been carried in the anniversary issue of EducationWorld)
Allahabad University is the fourth oldest modern university of India that was established in 1887 soon after the Presidency universities of Calcutta, Bombay and Madras were decreed in 1857. The university is the alma mater of three former prime ministers – Gulzari Lal Nanda, Chandra Shekhar and VP Singh, one president, two vice presidents, well-known authors, artists and senior bureaucrats. Once known as the Oxford of the East, the credit for conceiving a large Central College at Allahabad, eventually to develop into a university, goes to Sir William Muir. The campus is spread around the city with separate science and arts faculties and 10 affiliated colleges. (A special report on Allahabad University has been carried in the anniversary issue of EducationWorld)
Banaras Hindu University (Estb. 1916)
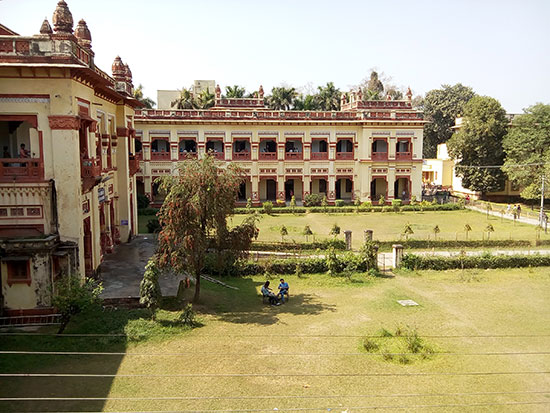 Located in Varanasi, the university was established in 1916 by Madan Mohan Malaviya a prominent lawyer and an Indian independence activist. Malviya believed that education is a catalyst for national awakening and keenly desired to establish a university. He publicly announced his desire at the 21st Conference of the Indian National Congress in Benares in December 1905. Eventually, with the support of Annie Besant, the university was set up in 1916. BHU is organised into 6 institutes and 14 faculties (streams) and about 140 departments. The university’s main campus, spread over 1300 acres, includes four interdisciplinary centres, a constituent college for women and three constituent schools.
Located in Varanasi, the university was established in 1916 by Madan Mohan Malaviya a prominent lawyer and an Indian independence activist. Malviya believed that education is a catalyst for national awakening and keenly desired to establish a university. He publicly announced his desire at the 21st Conference of the Indian National Congress in Benares in December 1905. Eventually, with the support of Annie Besant, the university was set up in 1916. BHU is organised into 6 institutes and 14 faculties (streams) and about 140 departments. The university’s main campus, spread over 1300 acres, includes four interdisciplinary centres, a constituent college for women and three constituent schools.
University of Mysore (Estb. 1916)
 The University of Mysore is the sixth oldest in the country and first in Karnataka. Established in 1916, the university was founded by Maharaja Nalvadi Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV and the then Diwan of Mysore Sir M. Visvesvaraya. The university boasts 226 affiliated colleges, 157 outreach /research centres, 66 recognised research centres, 8 training centres, and 47 specialised programmes, besides other courses.
The University of Mysore is the sixth oldest in the country and first in Karnataka. Established in 1916, the university was founded by Maharaja Nalvadi Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV and the then Diwan of Mysore Sir M. Visvesvaraya. The university boasts 226 affiliated colleges, 157 outreach /research centres, 66 recognised research centres, 8 training centres, and 47 specialised programmes, besides other courses.
Patna University (Estb. 1917)
 The first university of Bihar, Patna University was set up in 1917 at a time when the hold of conservatism was very strong in Bihar and the people of Bihar in general and the fairer sex in particular, were deprived of the advantages of higher education. The university’s jurisdiction extended to Bihar, Odisha, and Nepal for almost four decades until the establishment of the Tribhuvan University in Kathmandu and the Utkal University in Bhubaneshwar. In 1952, Patna University was revamped into a purely teaching-cum-residential university with its jurisdiction over metropolitan Patna. Today, 11 colleges are affiliated with this university and it boasts 31 postgraduate departments, 10 constituent colleges and four institutes under its wing.
The first university of Bihar, Patna University was set up in 1917 at a time when the hold of conservatism was very strong in Bihar and the people of Bihar in general and the fairer sex in particular, were deprived of the advantages of higher education. The university’s jurisdiction extended to Bihar, Odisha, and Nepal for almost four decades until the establishment of the Tribhuvan University in Kathmandu and the Utkal University in Bhubaneshwar. In 1952, Patna University was revamped into a purely teaching-cum-residential university with its jurisdiction over metropolitan Patna. Today, 11 colleges are affiliated with this university and it boasts 31 postgraduate departments, 10 constituent colleges and four institutes under its wing.